The Cortex-A5 processor implements the ARMv7-A architecture profile and can execute 32-bit ARM instructions and 16-bit and 32-bit Thumb instructions. Here are the top five things to know about Cortex-A5 processor.
1- Cortex-A5 is the smallest ARMv7 application processor
- The key design goals for Cortex-A5 were to design an ARMv7-A processor that was the size and power profile of an ARM926 (smallest ARMv5TEJ applications processor) but provided more performance than ARM1176 (which was the highest performance ARMv6 application processor). As a natural consequence of this design focus, the Cortex-A5 turned out to be the smallest application processor in the Cortex-A family.
- The other less obvious fact about Cortex-A5 is that it is highly configurable. For example, the instruction and data cache sizes can be configured in the range of 4KB-64KB. The smallest configuration with 4KB caches can be as tiny as 0.2 mm2 in 28nm process technology. This and other configurability options in Cortex-A5 enable designers to make right trade-offs for performance and cost for their targeted application.
2- Cortex-A5 is the lowest power application processor that runs a rich OS like Android
- One of the key design goals for Cortex-A5 was to achieve maximum energy efficiency and minimize power consumption. This resulted in the lowest power implementation of ARMv7-A architecture. The Cortex-A5 has a simple, in-order 8 stage pipeline and its microarchitecture is highly tuned to minimize power consumption.
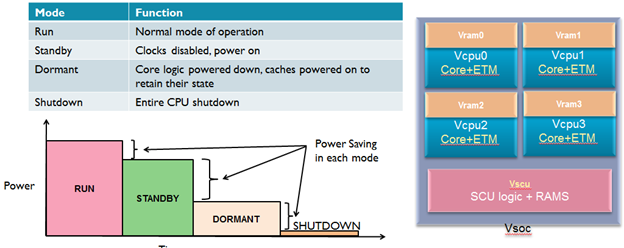
- Like other Cortex-A processors, the Cortex-A5 fully supports the low power modes like WFI, dormant and shut down. Combined with the small size of this processor, these low power modes enable aggressive leakage mitigation when implementing Cortex-A5 on the advanced process nodes (65nm and below)
3- Low cost, higher performance upgrade path for applications using classic ARM processors (like ARM926, ARM1176)
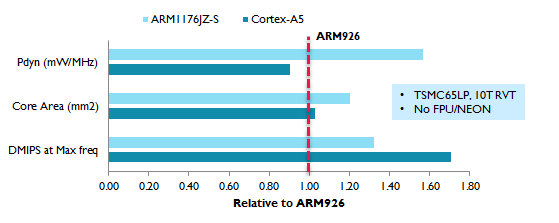
- The ARM9 is the most licensed processor in ARM’s history with over 250 licenses sold. It identified a very important power/cost sweet spot. The Cortex-A5 (launched in 2009) was designed to fit in the CPU same power and area footprint, while delivering significantly higher performance and power-efficiency, and bring it to modern ARMv7 feature set – software compatibility with the high end of the processor roadmap (then Cortex-A9). The Cortex-A5 supports the full feature set of Cortex-A9 at one third the area and about three-fourths the performance.
- The Cortex-A5 thus enabled the applications using classic ARM processors to migrate to ARMv7-A feature set and utilize the offerings of widespread ecosystem – at lower silicon cost, higher performance and modern ARMv7-A feature set.
 4- Cortex-A5 enabled a whole new category of mobile devices – the entry level smartphones
4- Cortex-A5 enabled a whole new category of mobile devices – the entry level smartphones
- The fact that Cortex-A5 supported the rich ARMv7-A features in a sweet power/performance/area spot made it an ideal choice with designers to build low cost, entry level smartphone devices. Furthermore, being fully software compatible with Cortex-A9 ensured that devices using Cortex-A5 can utilize the strong and vibrant ARMv7-A vibration ecosystem.
- Cortex-A5 defined and began the era of $100 entry smartphones couple of years back (2010-2011). More interestingly, it is enabling sub $100 tablets and $50 smartphones today!
5- Cortex-A5 is pioneering and defining new class of high end embedded applications with rich user interfaces today!
- Traditional embedded application markets are observing a trend of requiring more compute performance and connectivity requirements – but in very tight power and cost budgets. The Cortex-A5 is an ideal candidate for everything from single-board industrial computers to offload processors to the burgeoning IoT market and wearable devices. Two popular embedded platforms based on Cortex-A5 are Atmel’s SAMA5D3 and Freescale’s Vybrid platforms.





0 Comments